Essence of Project Management
Project management is a way to turn an idea into a result by effectively managing all stages of work. More specifically, it involves planning, organizing, managing resources, and controlling the execution of tasks to achieve specific project goals on time and within budget.
Project management is carried out through actions within processes that can be grouped into five categories:
- Initiation Processes;
- Planning Processes;
- Execution Processes;
- Monitoring & Control Processes;
- Closure Processes.
- Project Life Cycle
- Concept Diagram
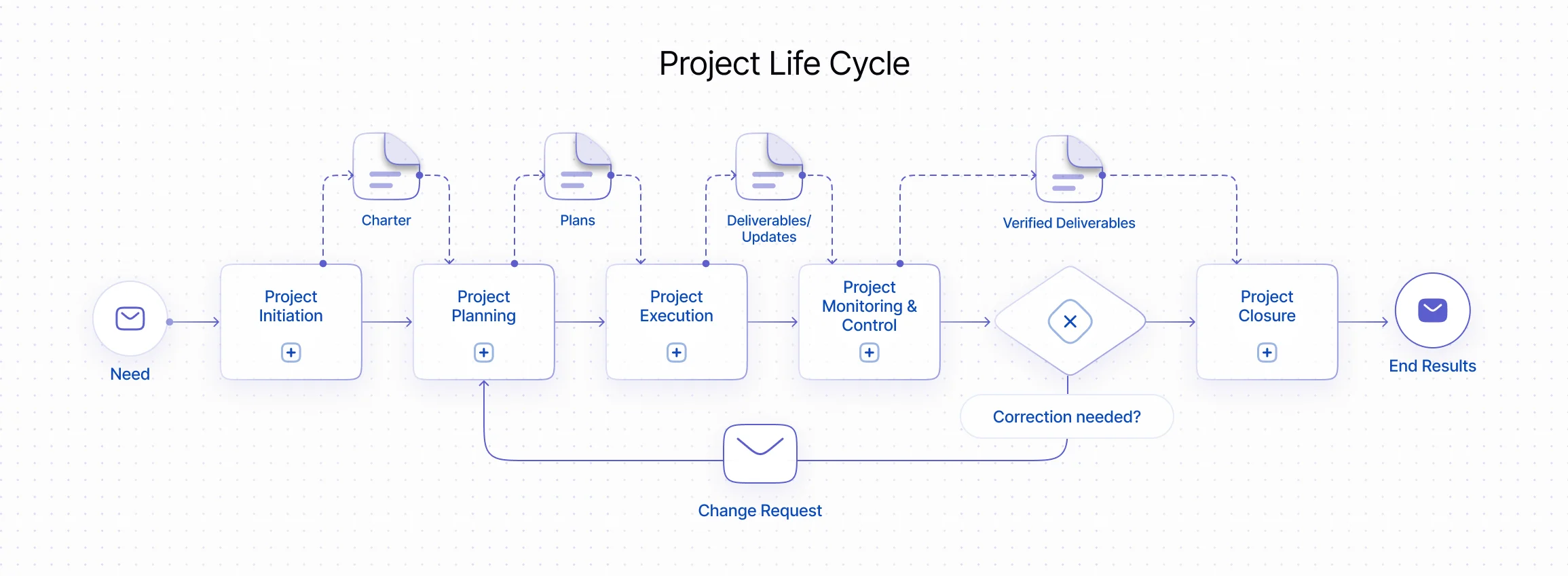
The essence of project management and process automation lies in the actions necessary to achieve successful outcomes and optimize the way work is done, considering various types of constraints and applied resources.
- Material;
- Cost;
- Labor/Work.
- Cost;
- Quality;
- Scope;
- Duration.
Project types
According to the Management Method, common classifications include:
Predictive (Waterfall)
All project elements are planned with a certain degree of accuracy at the initial stage.
Adaptive (Agile)
The project is planned with low accuracy at the initial stage and high accuracy for individual iterations (Sprints) as the work progresses.
Hybrid
Contains elements of both types, which allows the use of elements from predictive and adaptive types.
Other indicators are either calculated (e.g., Duration) or influenced by the primary factors (e.g., Risks).
In essence, effective project management entails proper planning, tracking of actual performance metrics, analyzing deviations, and making informed adjustments to the primary control parameters — while accounting for internal and external constraints and risks — in order to achieve the project's objectives.
Project Accounting is the process of systematically recording, tracking, and analyzing all data related to the execution of a project, including financial, time, and resource elements. It may involve recording expenses, tracking work hours, monitoring the use of materials and equipment, and ensuring compliance with budget and deadlines.
Therefore, it is a tool necessary for the implementation of the following functions:- Control of all project resources;
- Evaluation of the efficiency of resource utilization;
- Analysis of deviations between planned and actual data;
- Implementation of preventive or corrective actions.
Thus, Project Management and its Accounting are integral parts of the overall set of company management processes and involve the conscious operation of both quantitative (work, resources, hours, etc.) and financial (expenses, income) indicators of the company. Depending on the company's business, projects can serve as the main source of income or as a means of implementing changes (Change Management).
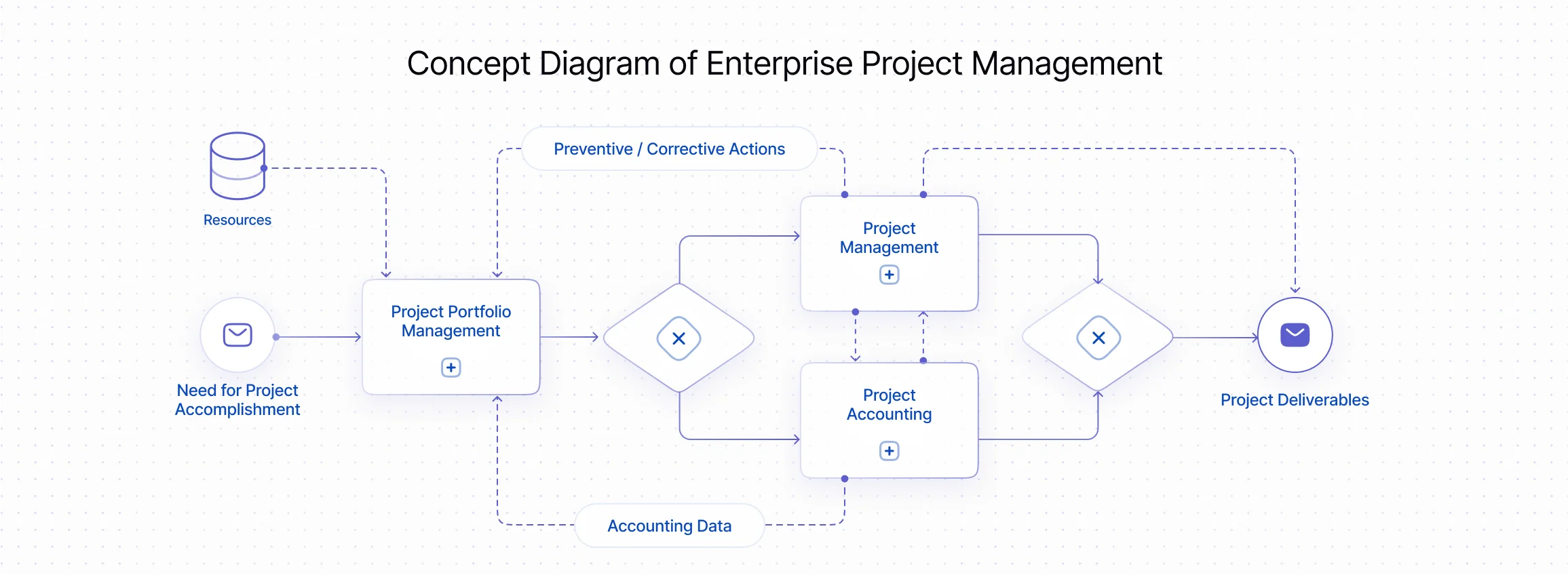
At the same time, project accounting related to quantitative indicators (such as recording actual labor effort, duration, etc.) is always considered primary that is, it is essential for the subsequent calculation of financial metrics (cash flow, cost of production, profit, etc.).
Essence of Project Automation
A modern, comprehensive project management automation system should cover:
- Project management;
- Data tracking during project execution.
Project management focuses on ensuring the successful completion of the project, meeting deadlines, achieving objectives, and optimizing resource utilization. In contrast, project tracking is more concerned with documentation and reporting, accounting for resources used, and cost control.
The system should provide the following processes:
This is the process of developing a detailed plan that includes a structured list of tasks required to achieve defined objectives. Using the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) tool allows a large-scale project to be divided into smaller, more manageable components.
This approach enhances understanding of specific tasks, their interdependencies, and enables more effective project management.
The depth of work decomposition and the principles of its division into logical elements should correspond to the needs of controlling these elements, as well as take into account possible links with elements of financial forecasting, budgeting, and cost accounting.
It is the process of determining what resources (people, equipment, materials) will be needed to complete the project tasks, as well as how much of each type of resource will be involved in the project.
This includes:
- Planning the number of work hours, the required amount of materials, taking into account their availability.
- Evaluating whether the necessary resources are available or need to be purchased or rented.
- Assigning resources to specific tasks and phases of the project.
- Aligning and optimizing resource allocation to ensure efficient utilization.
- Selection based on qualifications, skills, and availability for assignment to specific tasks according to the WBS.
Project duration refers to the total time required to complete a project from start to finish.
During the planning phase, several key steps are taken:
- Task duration estimation: Based on historical data, analogous projects, parameters, or expert judgment, the time required for each task is estimated. Potential delays caused by internal or external factors (such as resource constraints or budget issues) are also taken into account.
- Dependency analysis (Sequencing): Identifies which tasks are dependent on others and establishes the logical order of execution.
- Schedule development: A detailed project schedule is created using tools such as Gantt charts. This includes identifying which tasks can be performed in parallel and which must be completed sequentially.
This is a sequence of steps aimed at identifying and allocating the financial resources required to implement a project. A project budget may consist of the total cost of project activities as well as additional project-related expenses.
It represents the transformation of quantitative data calculated during earlier planning stages into a financial framework.
Budget planning includes:
- Determining the costs of performing each project task, including personnel, materials, equipment, rental, services, etc.
- Identifying sources of funding (own or credit funds).
- Planning the revenue to be obtained as a result of the project implementation. The budget is based on the planned value of services performed within the project.
- Distributing the total project budget across different tasks and stages to ensure the necessary financial resources for the successful completion of the work.
- Reviewing the prepared budget with the project team and stakeholders, making adjustments, and approving the final budget.
This involves the documentation of the execution of planned activities aimed at achieving the project objectives, specifically:
- Recording actual data on the volume of work performed in accordance with the project plan and the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
- Timely accounting of all project implementation costs, including entering data on raw material and supply purchases, recording incurred expenses, and preparing and approving timesheets.
- Monitoring the progress of work execution and reallocating resources when necessary.
- Controlling actual project expenditures by comparing them with the approved budget and taking corrective actions as required.
- Issuing invoices to clients based on recorded hours worked.
- Maintaining communication among team members through meeting scheduling and resource coordination.
Generating reports and data dashboards allows monitoring of the following key indicators:
- Materials: Reports enable tracking of material usage, identifying overconsumption or shortages.
- Labor Effort: Analysis of hours spent broken down by employees, teams, and tasks; identification of uneven workloads.
- Cost: Reports include information on total expenses, covering salaries, materials, equipment, and other resources.
- Revenue: Reflects the project’s financial results and projected profitability.
- Duration: Contains data on actual task completion times compared to planned schedules.
- Schedule: Dashboards display progress of task execution and key milestones.
- Utilization: Analysis of resource usage (human and material) to identify underutilized or overloaded resources.
These functions provide information on the relationship between planned and actual indicators across various parameters. Based on these data, problem sources can be identified, possible solutions determined, and information provided to stakeholders in the expected format.
Key monitoring areas:
- Plan Comparison: Actual data (costs, timelines, task completion) are compared against the plan.
- Trend Analysis: Patterns in task execution are studied to anticipate potential problems or delays.
- Forecasting: Data is used to generate forecasts for project completion, costs, and resource needs.
This process makes it possible to track data used to monitor deviations of actual expenses from those planned and can be performed both for the project as a whole and for individual stages.
Key areas of analysis:
- Actual expenses are compared with the project budget to identify overruns or savings.
- Factors causing variances (e.g., delays, scope changes, unexpected costs) are identified.
- Based on the analysis, recommendations are developed to optimize costs and minimize financial risks.
To extend the functionality of the system, specialized software products may be used:
- For portfolio management (Portfolio Management Systems);
- For task management (Task Management Systems);
- To enhance project communication (Communication Management Systems);
- For document management (Document Management Systems);
- For human resources management (HR Management Systems).
Project integration with other systems is a critical process that ensures effective interaction between different platforms, tools, and data sources.

Overview of the Project Management & Accounting within Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance
Capabilities of the software for automating project management processes within the D365FO Project Management & Accounting Module.
Implementation Scenarios for the Project Management & Accounting Module

Extension of D365FO
An extension of the existing ERP system, Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations Applications (Dynamics 365 Finance, Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management, Dynamics 365 Human Resources, Dynamics 365 Commerce) with the Project Management & Accounting functionality.

Migration to D365FO
Migration from an old version of the ERP system to Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations Apps through the initial implementation of the Project Management & Accounting module.
Impact on Business Indicators from the Automation of Project Management & Accounting Processes within D365FO Apps
Efficient use of resources
Optimal allocation of labor, materials, and equipment for project implementation, taking into account employee skills and availability. Integration with employee calendars, allowing for more accurate scheduling and avoiding conflicts.
Adaptability
Implementation and analysis of projects of any complexity and with any type of resources within a single project or in separate projects, within organizational units and/or across the entire organization. Configuring the system for the specific needs of the organization, including customization of business processes and reporting.
Integration
Project Мanagement & Accounting provides integration with other D365FO modules, allowing you to effectively manage projects, finances, resources, and customers in a single environment.
Detailed planning
With a work breakdown structure (WBS) and forecasting tools, the system allows you to plan tasks, resources, and budgets in detail, which helps avoid surprises and cost overruns.
Cost optimization
Cost control functionality allows you to carefully track the budget at each stage of the project and identify cost overruns in a timely manner.
Risk Minimization
Using dashboards and reports to monitor risks in real time allows you to respond quickly to changes.
Mobility
Access to the system from different devices provides flexibility and convenience of work, regardless of location.
Communication
The system ensures effective communication between project participants, which helps to avoid misunderstandings and delays.
Features of the D365FO Project Management & Accounting Module to Improve Projects Planning, Execution and Control in Your Organization
Seamless Integration with Other Modules
Project Management & Accounting module integrates with other Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations Applications modules (General ledger, Accounts Payable and Receivable, Procurement and Sourcing, Inventory and Warehouse Management, Human Resources, Sales and Marketing, Manufacturing, Analytics and Reporting) to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and visibility accross the organization.
Financial Planning and Control
Automation of project management and accounting processes within the Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations Apps ecosystem enables comprehensive solution to manage projects from inception to completion while ensuring financial control and visibility.
Speed and Simplicity of Implementation
Achieve the goals of implementing the D365FO ERP system's Project Management & Accounting module with minimal effort by automating project planning and execution, resource, time and expense management, billing and revenue recognition, budgeting and cost control processes within the D365FO Apps ecosystem.
Advanced Reporting and Analytics
With the powerful reporting and analytics tools within the Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations Apps ecosystem, Project Management & Accounting module provides capabilities to monitor project performance, financials, and resource utilization.
Integration with External Systems
Project Management & Accounting module in D365FO with predefined integration options, such as Data Entities, Data Import/Export Frameworks, Power Platform, API integrations can work harmoniously with other systems enhancing data flow and providing a unified view of business operations.

If you have any questions, you can request a consultation or receive additional materials
They trust us
About SMART business
SMART business — Your Microsoft Dynamics 365 Implementation Partner
We connect business processes and leverage Microsoft technologies and AI to help our customers succeed quickly and efficiently.
SMART business is a leading Microsoft partner in the development, implementation, and support of modern ERP, CRM, and HRM systems, as well as Microsoft cloud services and SMART solutions based on predictive analytics and machine learning.
Holding all six Microsoft Solutions Partner Designations, we apply best practices and the latest tools to accelerate the achievement of our customers’ strategic business goals.
• Extensive Microsoft Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations (formerly AX) ERP implementation expertise since 2008.
• Global reach: implementations and support in over 65 countries.
• ISO certifications: ISO 27001 (security), ISO 27701 (privacy), ISO 9001 (quality).
in the IT market
worldwide
by Microsoft
